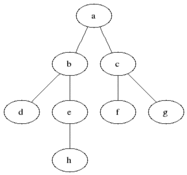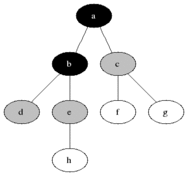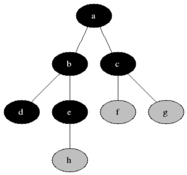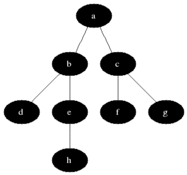
Breadth First Traversal is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. It starts at the tree root (or some arbitrary node of a graph, sometimes referred to as a 'search key') and explores the neighbor nodes first, before moving to the next level neighbors.
As in the example given above, BFS algorithm traverses from A to B to E to F first then to C and G lastly to D.
It employs the following rules.
Rule 1 − Visit the adjacent unvisited vertex. Mark it as visited. Display it. Insert it in a queue.
Rule 2 − If no adjacent vertex is found, remove the first vertex from the queue.
Rule 3 − Repeat Rule 1 and Rule 2 until the queue is empty.
At this stage, we are left with no unmarked (unvisited) nodes. But as per the algorithm we keep on dequeuing in order to get all unvisited nodes. When the queue gets emptied, the program is over.
Breadth-First-Search(Graph, root):
for each node n in Graph:
n.distance = INFINITY
n.parent = NIL
create empty queue Q
root.distance = 0
Q.enqueue(root)
while Q is not empty:
current = Q.dequeue()
for each node n that is adjacent to current:
if n.distance == INFINITY:
n.distance = current.distance + 1
n.parent = current
Q.enqueue(n)
Time complexity -The time complexity can be expressed as O(|V|+|E|), since every vertex and every edge will be explored in the worst case.|V| is the number of vertices and |E| is the number of edges in the graph. Note that O(|E|) may vary between O(1) and O(|V|^{2}), depending on how sparse the input graph is.
Space complexity - O(|V|), where |V| is the cardinality of the set of vertices (as said before). If the graph is represented by an adjacency list it occupies O(|V|+|E|) space in memory, while an adjacency matrix representation occupies O(|V|^{2})